Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko
Clays and Clay Minerals, 65(5), p.371 - 375, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:79.17(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sakuma, Hiroshi*; Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suehara, Shigeru*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Fujii, Naoki*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Honda, Akira
Clays and Clay Minerals, 65(4), p.252 - 272, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.51(Chemistry, Physical)Structure and stability of montmorillonite edge faces (110), (010), (100), and (130) of the layer charges y = 0.5 and 0.33 are investigated by the first-principles electronic calculations based on the density functional theory. Stacking and single layer models are tested for understanding the effect of stacking on the stability of montmorillonite edge faces. Most stacking layers stabilize the edge faces by making hydrogen bonds between the layers; therefore, the surface energy of stacking layers is reduced rather than the single layer model. This indicates that the surface energy of edge faces should be estimated depending on the swelling conditions. Lowest surface energies of (010) and (130) edge faces were realized by the presence of Mg ions on the edge faces. These edge faces have a strong adsorption site for cations due to local negative charge of the edges.
 sp
sp Laboratory, Sweden
Laboratory, SwedenSasamoto, Hiroshi; Isogai, Takeshi*; Kikuchi, Hirohito*; Sato, Hisao*; Svensson, D.*
Clay Minerals, 52(1), p.127 - 141, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:10.42(Chemistry, Physical)Compacted bentonite has been considered as a candidate of engineering barrier material in many countries for the safe disposal of high-level radioactive waste. SKB set up an in situ experiment (named ABM project) to compare the stability of different bentonites under the conditions exposed to an iron source and elevated temperature (up to 130 C as maximum) at the
C as maximum) at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory, Sweden. Results for the Japanese bentonite (Kunigel V1) are summarized in the present paper. Mineralogical investigation using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) suggested that no indication of smectite transformation or newly formed clay phases were observed. However, a distinct change of exchangeable cations of smectite was indicated (i.e., from Na type to Fe type) in the bentonite at the vicinity of the steel heater. Physical investigation by measurements of hydraulic conductivity and swelling property suggested that no significant change occur in the bentonite even at the vicinity of the steel heater. Such results might be considered due to the limited portion affected by the iron-bentonite interactions and partially occurred ion exchange reactions. Chemical investigation based on the measurements of methylane blue (MB), cation exchange capacity (CEC) and exchangeable cations showed that the lateral distribution for these parameters were basically constant without the significant gradient.
Hard Rock Laboratory, Sweden. Results for the Japanese bentonite (Kunigel V1) are summarized in the present paper. Mineralogical investigation using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) suggested that no indication of smectite transformation or newly formed clay phases were observed. However, a distinct change of exchangeable cations of smectite was indicated (i.e., from Na type to Fe type) in the bentonite at the vicinity of the steel heater. Physical investigation by measurements of hydraulic conductivity and swelling property suggested that no significant change occur in the bentonite even at the vicinity of the steel heater. Such results might be considered due to the limited portion affected by the iron-bentonite interactions and partially occurred ion exchange reactions. Chemical investigation based on the measurements of methylane blue (MB), cation exchange capacity (CEC) and exchangeable cations showed that the lateral distribution for these parameters were basically constant without the significant gradient.
 activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions [Clay Minerals, vol.51, p.275 (2016), Corrected Fig. 7.]
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions [Clay Minerals, vol.51, p.275 (2016), Corrected Fig. 7.]Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki
Clay Minerals, 51(5), P. 815, 2016/12
ERRATUM; Effects of OH activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions [Clay Minerals, vol.51, p.275 (2016), Corrected Fig. 7.]
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions [Clay Minerals, vol.51, p.275 (2016), Corrected Fig. 7.]
Kerisit, S.*; Okumura, Masahiko; Rosso, K. M.*; Machida, Masahiko
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(4), p.389 - 400, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:74.44(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditionsSawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.267 - 278, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.47(Chemistry, Physical)The dependences of the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite on activity of OH (a
(a -) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (
-) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (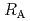 ) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as
) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as 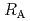 = 10
= 10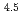 (a
(a -)
-)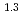 e
e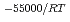 , was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures:
, was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures: 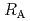 = 3500 (a
= 3500 (a -)
-)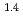 e
e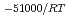 . The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a
. The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a - in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a
- in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a - is achieved somehow.
- is achieved somehow.
Ishidera, Takamitsu; Kurosawa, Seiichi*; Hayashi, Masanori*; Uchikoshi, Keiji*; Beppu, Hikari*
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.161 - 172, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.04(Chemistry, Physical)The sorption and diffusion behavior of Cs in illite-added compacted montmorillonite was investigated by through-diffusion experiment. The obtained distribution coefficient of Cs for the illite-added compacted montmorillonite was several times larger than that for the montmorillonite without illite, while no increase of effective diffusion coefficient was observed for the illite-added compacted montmorillonite. The dominant sorption site of Cs on illite is considered to be the frayed edge site (FES) considering the Cs concentration in this experiment. Therefore, the surface diffusion of Cs sorbing on the FES on illite surface was considered to be negligible in compacted montmorillonite.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Tamura, Hajimu*; Shibata, Kenji*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yasue, Kenichi; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji*
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(2), p.86 - 107, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:34.63(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sassi, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko
Clays and Clay Minerals, 64(2), p.108 - 114, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:21(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Hoshino, Seiichi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.279 - 287, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.47(Chemistry, Physical)Alteration of bentonite-cement interfaces and accompanying changes in diffusivity of tritiated water was experimentally investigated using intact hardened cement specimens. The alteration by carbonate solution was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 70% of the initial value after 180-day period. Another alteration under silicate system contacting hardened cement and compacted bentonite was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 71% of the initial value after 600-day period. The changes in the diffusivity were much less than those observed for mixed specimens of granulated hardened cement and bentonite where the diffusivity decreased down to 20% of the initial value over 180 days. The results were extrapolated to 15 years under simple assumptions and showed good agreement with those observed in the cement-argillite interface at Tournemire URL. Such an explanation enhances our confidence in our assessment of alteration of cement-bentonite systems and can be a base for using our data and models in long term assessment of radioactive waste disposal.
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Iida, Yoshihisa; Tanaka, Tadao; Kitagawa, Isamu
Clay Minerals, 48(2), p.411 - 422, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.52(Chemistry, Physical)Diffusive transport of Cs in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures was studied by a through diffusion method. Experiments were performed under variable aqueous compositions. Effective diffusivity (
in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures was studied by a through diffusion method. Experiments were performed under variable aqueous compositions. Effective diffusivity (
 ) values of 5.2E-10
) values of 5.2E-10 5.9E-9 m
5.9E-9 m s
s were obtained. The variation was somewhat large in the
were obtained. The variation was somewhat large in the 
 values. Apparent diffusivity (
values. Apparent diffusivity (
 ) values, on the other hand, were 2.0E-12
) values, on the other hand, were 2.0E-12  6.2E-12 m
6.2E-12 m s
s , which shows small variation. The results indicate that, in applying Fick's 1st law of diffusion, diffusive flux is proportional to the apparent concentration gradient of Cs in the sand-bentonite mixture rather than the gradient of Cs concentration in pore water. Since the apparent concentration gradient in sand-bentonite mixtures is nearly equal to the gradient of adsorbed Cs, diffusion of Cs under adsorbed state would be the main mechanism of diffusion of Cs in sand-bentonite mixtures.
, which shows small variation. The results indicate that, in applying Fick's 1st law of diffusion, diffusive flux is proportional to the apparent concentration gradient of Cs in the sand-bentonite mixture rather than the gradient of Cs concentration in pore water. Since the apparent concentration gradient in sand-bentonite mixtures is nearly equal to the gradient of adsorbed Cs, diffusion of Cs under adsorbed state would be the main mechanism of diffusion of Cs in sand-bentonite mixtures.
 concrete/clay interactions at the Tournemire URL
concrete/clay interactions at the Tournemire URLYamaguchi, Tetsuji; Kataoka, Masaharu; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Mukai, Masayuki; Hoshino, Seiichi; Tanaka, Tadao; Marsal, F.*; Pellegrini, D.*
Clay Minerals, 48(2), p.185 - 197, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.54(Chemistry, Physical)Highly alkaline environments induced by cement based materials are likely to deteriorate the physical and/or chemical properties of the bentonite buffer materials in radioactive waste repositories. Predicting long-term alteration of concrete/clay systems requires physico-chemical models and a number of input parameters. In order to provide reliability to the long-term prediction of bentonite buffer performance under disposal conditions, it is necessary to develop and verify reactive transport codes for concrete/clay systems. In this study, a PHREEQC-based, reactive transport analysis code (MC-CEMENT ver.2) was developed and was verified by comparing results of the calculations with  observations of the mineralogical evolution at the concrete/argillite interface. The calculation reproduced the observations such as the mineralogical changes limited within one cm in thickness, formation of CaCO
observations of the mineralogical evolution at the concrete/argillite interface. The calculation reproduced the observations such as the mineralogical changes limited within one cm in thickness, formation of CaCO and CSH, dissolution of quartz, decrease of porosity in argillite and increase in concrete. These agreements indicate possibility that the models based on lab-scale (
and CSH, dissolution of quartz, decrease of porosity in argillite and increase in concrete. These agreements indicate possibility that the models based on lab-scale ( 1 y) experiments can be applied to longer time scale. The fact that the calculation did not reproduce the dissolution of clays and the formation of gypsum indicates that there is still room for improvement in our model.
1 y) experiments can be applied to longer time scale. The fact that the calculation did not reproduce the dissolution of clays and the formation of gypsum indicates that there is still room for improvement in our model.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Kadowaki, Mitsushi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Clay Minerals, 48(2), p.403 - 410, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:23.68(Chemistry, Physical)Montmorillonite is the main constituent of bentonite clay buffer materials in radioactive waste repositories. Highly alkaline environments induced by cement based materials are likely to alter montmorillonite, and to deteriorate the physical and/or chemical properties of the buffer materials. The deterioration may cause variation in hydraulic conductivity of the buffer and induce major uncertainties in the radionuclide migration analysis. Empirical data on the variation of hydraulic conductivity are, however, scarce mainly because the alteration of compacted buffer materials, sand-bentonite mixture specimen, is extremely slow. In this study, laboratory experiments were performed to observe changes in hydraulic conductivity of sand-bentonite mixtures accompanied with their alkaline alteration using NaOH based solutions at 80-90  C. Three types of experiments proved that the alkaline alteration of bentonite buffer can increase the hydraulic conductivity. The data obtained in this study are useful for verification of the code that will be used for assessing the alteration.
C. Three types of experiments proved that the alkaline alteration of bentonite buffer can increase the hydraulic conductivity. The data obtained in this study are useful for verification of the code that will be used for assessing the alteration.
Arthur, R. C.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Walker, C.; Yui, Mikazu
Clays and Clay Minerals, 59(6), p.626 - 639, 2011/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:45.29(Chemistry, Physical)Regarding to geological disposal of high level radioactive waste, long-term evolution of chemical condition in the rock mass by interactions of cementitious grout and rock would be predicted, if the grout is used for reducing the groundwater inflow during construction of drifts. Evolution of chemical condition is important because it could affect the evaluation of radionuclides migration for performance assessment. Zeolite is one of important alteration minerals by interactions of cementitious grout and rock. For evaluation of long-term evolution of chemical condition, it is necessary to develop thermodynamic data for alteration minerals like zeolite. The present paper proposes a revised model to derive more reliable thermodynamic data for zeolite. Additionally, a possibility to apply this revised model on other important alteration minerals is suggested.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Hards, V. L.*; Milodo, A. E.*; West, J. M.*; Bateman, K.*; Coombs, P.*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Wetton, P. D.*; Yoshida, Hidekazu; Aoki, Kazuhiro
Clay Minerals, 36(4), p.599 - 613, 2001/00
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:57.14(Chemistry, Physical)None
Nagano, Tetsushi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Nakayama, Shinichi; Nakashima, Satoru*
Clays and Clay Minerals, 47(6), p.748 - 754, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:44.62(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Murakami, Takashi*; Isobe, Hiroshi; Sato, Tsutomu; Onuki, Toshihiko
Clays and Clay Minerals, 44(2), p.244 - 256, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:84.43(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sato, Tsutomu; Murakami, Takashi*; Watanabe, Takashi*
Clays and Clay Minerals, 44(4), p.460 - 469, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:75.43(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Nagano, Tetsushi; *; ;
Clays and Clay Minerals, 42(2), p.226 - 234, 1994/00
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:75.61(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 C
CNagano, Tetsushi; *; ; *;
Clays and Clay Minerals, 40(5), p.600 - 607, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:74.64(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English